In an era dominated by digital transformation, the demand for cyber insurance has surged as organizations grapple with the evolving threat landscape. As underwriters strive to stay ahead, they face a myriad of risks, emerging trends and formidable challenges in crafting robust policies. This article explores the intricacies of underwriting cyber insurance policies, shedding light on the evolving landscape.
Rising Risks in Cyber Insurance Underwriting:
- Cybersecurity threats evolution:
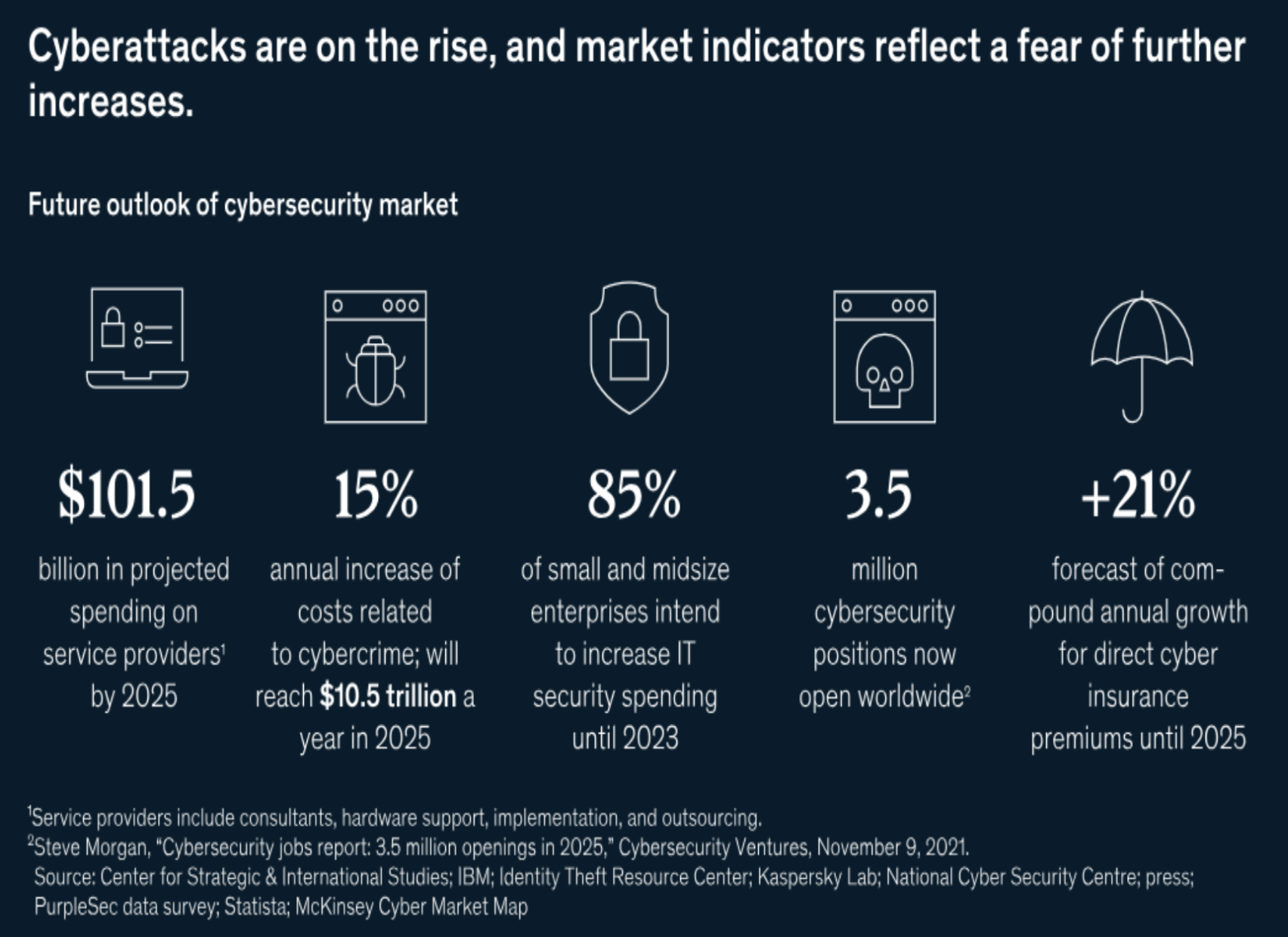
Exhibit 1: Source McKinsey & Co.
The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats poses a considerable challenge for underwriters.
According to a report put out by the U.S. government, over 4,000 ransomware attacks happen every day. This makes it the most prominent method of malware to date.
As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, underwriting must adapt to anticipate and mitigate risks associated with advanced persistent threats, ransomware attacks and other malicious activities.
- Data Privacy Regulations:
The tightening grip of data protection regulations worldwide adds a layer of complexity to underwriting. Insurers must navigate the intricacies of compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA, considering the potential financial impact of non-compliance for both the insured and the insurer.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities:
With the increasing connectedness of businesses, the risks associated with third-party vendors and supply chain partners are on the rise. Underwriters must scrutinize the cyber hygiene of connected entities, as a security lapse in one can have cascading effects on others.
See also: Cyber Insurance Market Hardens
Trends Shaping Cyber Insurance Underwriting:
- AI and Predictive Analytics:
Leveraging artificial intelligence and predictive analytics is becoming pivotal in underwriting. By analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, underwriters can better assess risk profiles and price policies more accurately, staying one step ahead of potential cyber threats.
- Parametric Insurance Models:
Parametric insurance, which pays out based on predefined parameters rather than actual losses, is gaining traction. This innovative approach can streamline the claims process, providing faster payouts and better aligning with the fast-paced nature of cyber incidents.
- Cybersecurity Assessments and Audits:
Insurers are increasingly incorporating cybersecurity assessments and audits into their underwriting processes. This approach helps in understanding an organization's cybersecurity posture, enabling underwriters to tailor policies to specific risk profiles.
Challenges in Cyber Insurance Underwriting:
- Lack of Standardization:
The absence of standardized frameworks for assessing cyber risks makes underwriting challenging. Differing methodologies and criteria among insurers can lead to inconsistencies in risk evaluation, hindering the establishment of a cohesive and transparent market.
- Limited Historical Data:
Unlike traditional insurance, cyber insurance lacks a robust history of claims data. The scarcity of historical data makes it difficult for underwriters to accurately predict and price cyber risks. Developing models that can effectively navigate this uncertainty remains a significant challenge.
- Dynamic Regulatory Environment:
The rapid evolution of data protection and privacy regulations globally poses a continuing challenge. Underwriters must stay agile to adapt policies to comply with ever-changing legal landscapes, adding a layer of complexity to an already intricate process.
See also: Cyber Insurance at Inflection Point
Mitigating Risks and Meeting Challenges:
- Collaboration and Information Sharing:
Collaborative efforts among insurers, businesses and cybersecurity experts can enhance collective resilience. Sharing threat intelligence and best practices can help create a more informed underwriting process, fostering a united front against cyber threats.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
To stay ahead in the cyber insurance landscape, underwriters must embrace a culture of continuous learning. Regular training and updates on emerging threats and technologies can equip underwriters to make informed decisions in an ever-changing environment.
- Technology Integration:
The integration of cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and machine learning can enhance the efficiency of underwriting processes. Blockchain, for instance, can provide a secure and transparent platform for managing policy data, while machine learning can improve risk assessment accuracy.
Conclusion:
Navigating the complex world of cyber insurance underwriting demands balancing understanding evolving risks, embracing emerging trends and overcoming formidable challenges. As the digital landscape continues to transform, underwriters must evolve their methodologies, leveraging technology, collaboration and continuous learning to craft policies that provide effective protection against the ever-growing specter of cyber threats. Only through an adaptive approach can the insurance industry effectively manage and mitigate the risks associated with the digital age.